Albedo plays a crucial role in understanding Earth's climate system and energy balance. It refers to the measure of how much sunlight is reflected by a surface or object. This concept is vital for scientists, meteorologists, and environmentalists who study global warming, climate change, and weather patterns. By delving deeper into albedo, we can gain insights into the mechanisms that regulate our planet's temperature and its response to external forces.
Earth's climate is a complex system influenced by various factors, and albedo is one of the key components that contribute to its stability or instability. Understanding how albedo works can help us predict future climate scenarios and develop strategies to mitigate the impacts of climate change. This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of albedo, its significance, and its applications in different fields.
Whether you're a student, researcher, or simply someone curious about the environment, this guide will walk you through the basics of albedo, its effects on the planet, and its relevance to modern climate science. Let's explore the fascinating world of albedo together.
Read also:Brenda Fehr The Rising Star In The World Of Entertainment
Table of Contents
- What is Albedo?
- Types of Albedo
- Albedo and Climate
- Measuring Albedo
- Effects of Albedo
- Albedo Feedback Mechanisms
- Human Impact on Albedo
- Modeling Albedo
- Albedo in Space
- Conclusion
What is Albedo?
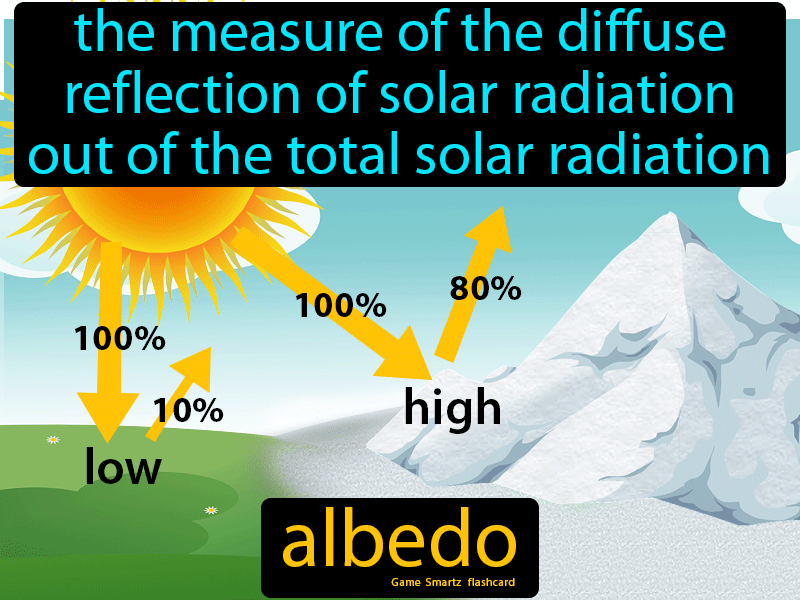
Albedo is a dimensionless quantity that represents the fraction of solar energy reflected by a surface or object. It is expressed as a value between 0 and 1, where 0 indicates complete absorption of sunlight, and 1 indicates total reflection. For example, fresh snow has a high albedo, often around 0.8-0.9, meaning it reflects up to 90% of the sunlight that hits it. In contrast, dark surfaces like asphalt have low albedo values, typically around 0.05-0.15, absorbing most of the sunlight.
Albedo is influenced by several factors, including the color, texture, and composition of the surface. It is an essential parameter in climate science because it determines how much solar radiation is absorbed or reflected by the Earth's surface, affecting the planet's overall temperature.
Why is Albedo Important?
- Albedo influences the Earth's energy balance.
- It affects the distribution of heat across the planet.
- Changes in albedo can amplify or mitigate climate change.
Types of Albedo
There are different types of albedo, each with its own significance in climate studies:
Bond Albedo
Bond albedo refers to the total reflectivity of a planet, moon, or other celestial body. It is calculated by considering all wavelengths of light and is used to study the overall energy budget of a celestial object.
Directional Albedo
Directional albedo measures the reflectivity of a surface in a specific direction. This type of albedo is important for understanding how light interacts with surfaces at different angles.
Surface Albedo
Surface albedo pertains to the reflectivity of the Earth's surface, such as land, water, and ice. It is a critical factor in determining regional climate patterns and the effects of land use changes.
Read also:Orville Peck Lpsg Unveiling The Enigma Of Country Musics Rising Star
Albedo and Climate
Albedo is intricately linked to the Earth's climate system. Changes in albedo can lead to significant alterations in the planet's temperature and weather patterns. For instance, the melting of polar ice caps reduces the Earth's albedo, causing more solar radiation to be absorbed and contributing to global warming.
According to NASA, the Earth's average albedo is approximately 0.3, meaning that about 30% of incoming solar radiation is reflected back into space. However, this value can vary depending on factors such as cloud cover, vegetation, and urbanization.
How Albedo Affects Climate
- High albedo surfaces, like ice and snow, reflect more sunlight, cooling the surrounding area.
- Low albedo surfaces, such as oceans and forests, absorb more sunlight, warming the environment.
- Changes in land use, such as deforestation or urban expansion, can alter local albedo and impact regional climates.
Measuring Albedo
Measuring albedo involves using advanced instruments and techniques to quantify the reflectivity of surfaces. Satellites, ground-based sensors, and airborne platforms are commonly employed to collect albedo data. These measurements are then used to create maps and models that help scientists understand the Earth's energy balance and climate dynamics.
One of the most prominent satellite missions for measuring albedo is NASA's Clouds and the Earth's Radiant Energy System (CERES), which provides detailed information about the Earth's radiation budget.
Techniques for Measuring Albedo
- Remote sensing using satellites.
- Ground-based radiometers.
- Aerial surveys with drones or aircraft.
Effects of Albedo
The effects of albedo are far-reaching and impact various aspects of the Earth's environment. From influencing global temperatures to affecting local weather patterns, albedo plays a pivotal role in shaping the planet's climate. Here are some key effects:
Global Warming
As ice and snow melt due to rising temperatures, the Earth's albedo decreases, leading to more heat absorption and further warming. This feedback loop, known as the ice-albedo feedback, is one of the primary drivers of global warming.
Regional Climate Variability
Changes in albedo can cause variations in regional climates. For example, urban heat islands, characterized by low albedo surfaces like concrete and asphalt, experience higher temperatures compared to surrounding rural areas.
Albedo Feedback Mechanisms
Albedo feedback mechanisms are processes that amplify or dampen the effects of climate change. These mechanisms operate on both local and global scales and can have significant consequences for the Earth's climate system.
Positive Feedback
A positive feedback loop occurs when a change in albedo leads to further changes that enhance the initial effect. For instance, melting ice reduces albedo, causing more heat absorption, which in turn accelerates ice melt.
Negative Feedback
Negative feedback mechanisms work to counteract changes in albedo. For example, increased cloud cover can reflect more sunlight, offsetting the effects of reduced surface albedo.
Human Impact on Albedo
Human activities, such as deforestation, urbanization, and agriculture, can significantly alter the Earth's albedo. These changes can have both direct and indirect effects on the climate, influencing temperature patterns, precipitation, and weather systems.
Urbanization
Cities and urban areas often have lower albedo due to the prevalence of dark surfaces like roads and buildings. This contributes to the urban heat island effect, where cities experience higher temperatures compared to surrounding rural areas.
Land Use Changes
Converting forests into agricultural land or urban areas can reduce albedo, leading to increased heat absorption and local warming. On the other hand, reforestation and green roofs can increase albedo, mitigating some of the effects of climate change.
Modeling Albedo
Scientists use sophisticated models to simulate and predict the effects of albedo on the Earth's climate. These models incorporate data from various sources, including satellite observations, ground-based measurements, and historical records, to create accurate representations of the Earth's energy balance.
One of the most widely used models is the Community Earth System Model (CESM), developed by the National Center for Atmospheric Research (NCAR). CESM incorporates albedo data to simulate climate scenarios and assess the impacts of various factors on the Earth's climate system.
Albedo in Space
Albedo is not only relevant to Earth but also plays a crucial role in studying other celestial bodies. By measuring the albedo of planets, moons, and asteroids, scientists can gain insights into their composition, surface properties, and potential habitability.
For example, the Moon has an average albedo of about 0.12, meaning it reflects approximately 12% of the sunlight that hits it. In contrast, Venus has a high albedo of around 0.75, making it one of the brightest objects in the night sky.
Conclusion
Albedo is a fundamental concept in climate science that plays a vital role in regulating the Earth's temperature and energy balance. Understanding albedo and its effects can help us address the challenges posed by climate change and develop strategies to mitigate its impacts.
As we have seen, albedo influences global and regional climates, interacts with other climate factors, and is affected by human activities. By studying albedo and its feedback mechanisms, scientists can improve climate models and predictions, enabling us to make informed decisions about the future of our planet.
We invite you to share your thoughts and questions in the comments section below. Feel free to explore other articles on our website for more insights into climate science and related topics. Together, we can contribute to a better understanding of our planet and its environment.